Listen to this post:
Our grandparents and great grandparents produced much of their own food in their gardens or on their farms. Food choices in stores were limited, with little frozen food available and fewer fresh and canned foods for sale.
In 1850, most Americans (64%) worked on farms. [1] In 1900 there were 6 million US farms, with an average size of 150 acres. [2] By 1920, 30% of US workers still did farm work. [3] But after World War 2, the US government adopted policies that reduced the number of farmers and expanded the size of farms — for more efficiency, it was said. [4] Today, only 1% of Americans work on farms [5] and the number of farms in the U.S. has dropped by two thirds.
While the average size of the 2 million US farms today is 440 acres, most US farmland belongs to large farms that are over 2,000 acres in size, or more than 3 square miles. Many belong to corporations, not to those who farm them.
Along with efficiency came worsening food quality. Depleted soils produced less nutritious foods, while chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides contain neurotoxins and carcinogens that are ingested with the foods we eat.
Decades of consolidation of food production, processing and distribution has steadily increased the size and power of a small group of global agricultural corporations. Most of those companies are in turn members of the WEF [6], which is wielding unelected power to influence food production and distribution in the name of climate change, sustainability [7], health, and equity. [8]
For example, the WEF had this to say about the outlook for food systems in 2022:
Food systems account for up to one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions and are failing 768 million people living in hunger. In the face of volatile global shocks from conflicts such as the war in Ukraine, the COVID-19 pandemic, and extreme weather events, it has become more urgent than ever to transition food systems to a net-zero, nature-positive infrastructure that nourishes and feeds everyone. [9]
(Emphasis added)
However, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) disagrees with the WEF’s claim that up to one-third of greenhouse gas emissions are due to farming. The EPA says it is only 10%. [10] See the EPA’s graphic below.
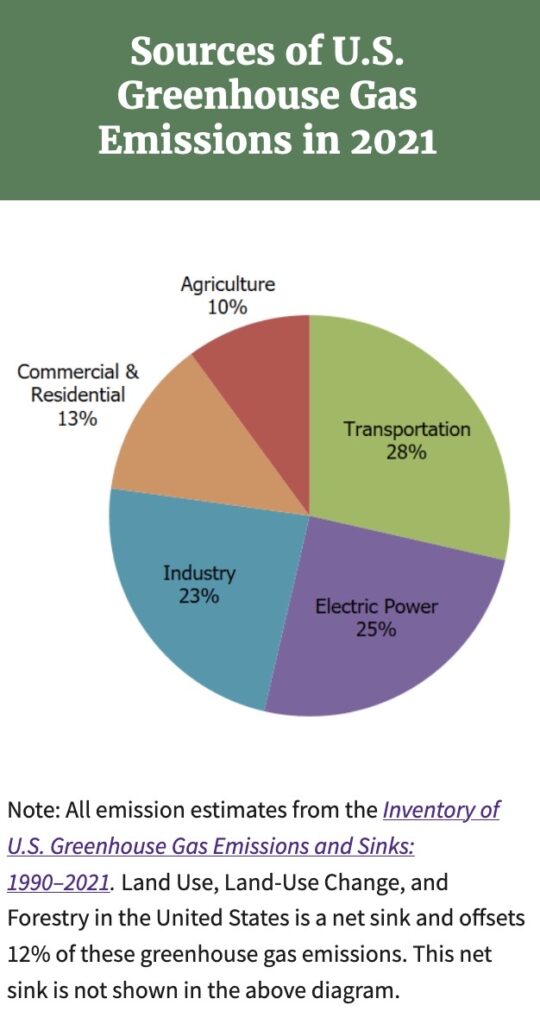
Are cows being given a bad rap for reasons other than belching the greenhouse gas methane? The WEF, UN [11] and other international entities have targeted the amount of meat humans consume and claim that a major reduction in the number of livestock is necessary to reduce greenhouse gases and global warming. Suggestions have been made to use insects as a protein replacement. One WEF White paper has this to say about insect consumption:
Insects, especially beetles, caterpillars, bees, wasps, ants, grasshoppers, locusts, termites and crickets, as well as other land-based invertebrates such as snails, earthworms and spiders, have been collected from the wild and eaten by communities throughout the world for thousands of years, especially in Africa, Asia and Latin America.
Compared to traditional livestock, insects and other invertebrates are more efficient at converting feed to meat. Insects require little land, water and labour, generate few greenhouse gases and raise few animal welfare issues. They are particularly good for converting waste to feed, thus supporting a circular bioeconomy as discussed in the section “Enablers for transformation.”
[12] , page 18
Organic agriculture, in which topsoil is rebuilt through composting and other means, can sequester more CO2 in the soil, trees and other plants than is lost through other agricultural processes. The EPA graphic (above) agrees, noting that forestry and forms of land use provide a “net sink” that reduces carbon dioxide emissions.
Feeding cows seaweed reduces their release of methane. [13]
But the potential climate advantage of transitioning to organic farming and using seaweed for fodder is ignored in calculations that demand farmers cull their herds.
The world’s largest food producers, processors, and retail sellers are joined with governments and NGOs through the WHO, UN, WEF, and a plethora of interconnected organizations, all focused on reducing or eliminating livestock. They want humans to convert to a state-directed diet comprised instead of synthetic meats, insects, and other food substitutes manufactured by these companies [14].
Many question whether this group of global industrialists and politicians will “improve the state of the world,” but there is no question that their intention is to consolidate and control global food production and distribution, thereby improving the state of member corporations’ profits. GMO crops and related chemical applications will be increased under pretense of climate rescue [15]; synthetic meats will be favored in government food programs; small farms will be shuttered.
This coordinated justification for global/government food control is presented in the name of sustainability, reducing the temperature, improving animal welfare, nurturing human health, and improving equity. However, there is no evidence it does even one of these things.
Regardless of what proportion of supposed greenhouse gases are being generated by agriculture, increasing local food supplies and regenerative agricultural practices offers numerous benefits to both humans and climate.
[1] https://www.nytimes.com/1988/07/20/us/farm-population-lowest-since-1850-s.html
[2] https://www.census.gov/library/publications/1902/dec/vol-05-agriculture.html
[3] https://www.nytimes.com/1988/07/20/us/farm-population-lowest-since-1850-s.html
[4] https://books.google.com/books?id=oL2v87Rx2QQC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
[5] https://usafacts.org/articles/farmer-demographics/
[6] https://www.weforum.org/partners#search
[7] https://www.foodactionalliance.org/home
[8] https://www.foodactionalliance.org/partners
[9] https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/02/food-systems-2022-outlook/
[10] https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks
[11] https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/08/global-meat-consumption-reduce-mitigate-effects-global-warming/
[12] https://www3.weforum.org/docs/White_Paper_Livestock_Emerging%20Economies.pdf
[13] https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/mar/18/cows-seaweed-methane-emissions-scientists
[14] https://www.foodactionalliance.org/partners
[15] https://www.globalresearch.ca/myth-gmos-saving-planet/5804013






![SUPPORT: Custom Meat Pilot Program – Sec. 12114 [Farm Bill]](https://doortofreedom.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/th-320084448.jpg)